Menstruation is a natural process marking a woman’s reproductive years. However, understanding menstrual health is crucial for maintaining a quality life. Menstrual health significantly affects a woman’s physical, emotional, and mental well-being. It’s more than just bleeding; it’s a reflection of hormonal balance and general health.
One common condition affecting this balance is menorrhagia. Defined as prolonged menstrual bleeding or excessively heavy periods, it can lead to discomfort, embarrassment, and even potential health risks. Women with menorrhagia may experience severe blood loss from heavy periods that interrupts daily activities, requires frequent lifestyle adjustments, and often induces fatigue. These interruptions can affect work, social activities, and personal life.
Understanding what menorrhagia means, its symptoms, and treatments help women make informed decisions. Recognition of these signs can prompt timely medical consultation, leading to effective management. This guidance aims to offer insights into recognizing, coping with, and treating this common yet challenging condition.
Identifying Menorrhagia: Symptoms and Deviations from Normalcy
Menorrhagia significantly deviates from normal menstrual bleeding. It’s characterized by menorrhagia heavy bleeding that is more intense than typical menstruation. If a woman finds her periods consistently lasting more than seven days, this may be an indication of heavy bleeding menorrhagia.
Symptoms may include: – Heavy period blood flow requiring multiple pad changes in a day – Heavy period blood loss that may lead to fatigue or anemia – Frequent passing of large blood clots – Prolonged menstrual bleeding, extending beyond a week
Distinguishing between a heavy period meaning manageable inconvenience and a severe condition is vital. Awareness of prolonged bleeding helps in recognizing when to seek medical guidance. With potential health impacts involving anemia or severe discomfort, understanding these signs ensures timely intervention.
Root Causes and Underlying Health Conditions
The origins of menorrhagia can be multifaceted. Often influenced by hormonal imbalances, other medical conditions also play roles. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), fibroids, and thyroid issues are significant contributors to this condition.
- Hormonal imbalances: An imbalance between estrogen and progesterone can cause the uterine lining to thicken excessively, resulting in profuse menstrual bleeding.
- Fibroids: Noncancerous growths in the uterus, fibroids are often found in women experiencing heavy periods.
- PCOS and other health conditions: Conditions like endometriosis can exacerbate menorrhagia bleeding.
Beyond medical conditions, lifestyle choices and cultural influences also play roles. Dietary habits lacking iron or essential nutrients can lead to or worsen heavy menses. Cultural beliefs about menstruation could delay medical consultation, exacerbating the condition.
Treatment, Modern Approaches, and Alternative Therapies
Managing menorrhagia involves a combination of traditional and alternative approaches. Conventional treatments include medicine for menorrhagia as well as surgical interventions.
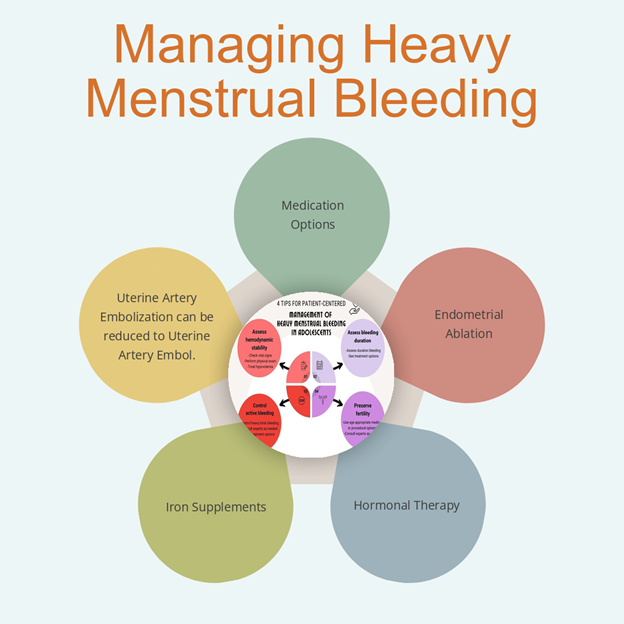
- Hormonal therapies: These may include birth control pills or hormonal IUDs like Mirena to help regulate periods.
- Surgical options: For severe cases, procedures like endometrial ablation can reduce the uterine lining to curtail bleeding.
Take Charge of Your Menstrual Health with Mansha Diagnostics
If you’re experiencing heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, don’t wait to seek answers. At Mansha Diagnostics, we offer comprehensive testing and expert guidance to help diagnose and manage menorrhagia effectively.
Book your consultation today and take the first step towards better menstrual health and overall well-being!
Emotional, Psychological, and Practical Coping Mechanisms
Women dealing with heavy menses often encounter emotional and psychological challenges. The stigma associated with menstrual bleeding can lead to feelings of shame or isolation.
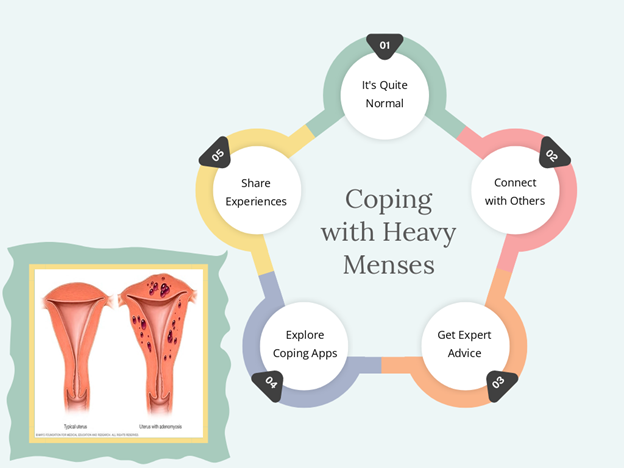
To cope: – Join support groups to share experiences and seek comfort – Seek professional counseling to address emotional impacts – Participate in open dialogues to de-stigmatize menorrhagia
Practical strategies are essential too: – Incorporate a balanced diet rich in iron to counteract heavy period blood loss – Engage in light exercise to improve mood and reduce symptoms – Adopt lifestyle changes that include scheduled rest and mindfulness
These coping mechanisms provide comprehensive support, addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of menorrhagia.
When to See a Doctor: Recognizing the Red Flags
Certain signs necessitate medical consultation. If you experience heavy heavy periods with blood clots or have persistent painful heavy periods, it’s time to see a healthcare provider.
Don’t ignore these red flags: – Heavy period flow and blood clots beyond seven days – Severe cramping accompanying heavy period blood
Seeking medical advice can prevent complications and lead to effective management. Speaking openly about menstrual health encourages timely treatment, helping overcome societal taboos and ensuring that women receive the care they need.


